What is a microwave PCB?
For some specific applications, where high frequency is required, the microwave circuit is the appropriate solution.
The printed circuit board is then a component in its own right, integrating functions such as filters, antennas, or others.
Materials are chosen mainly based on their dielectric properties We can help you find the right material for you. Through our subsidiary Elliptika, we can design, build, and test the complex functions that will form the heart of your microwave circuit.
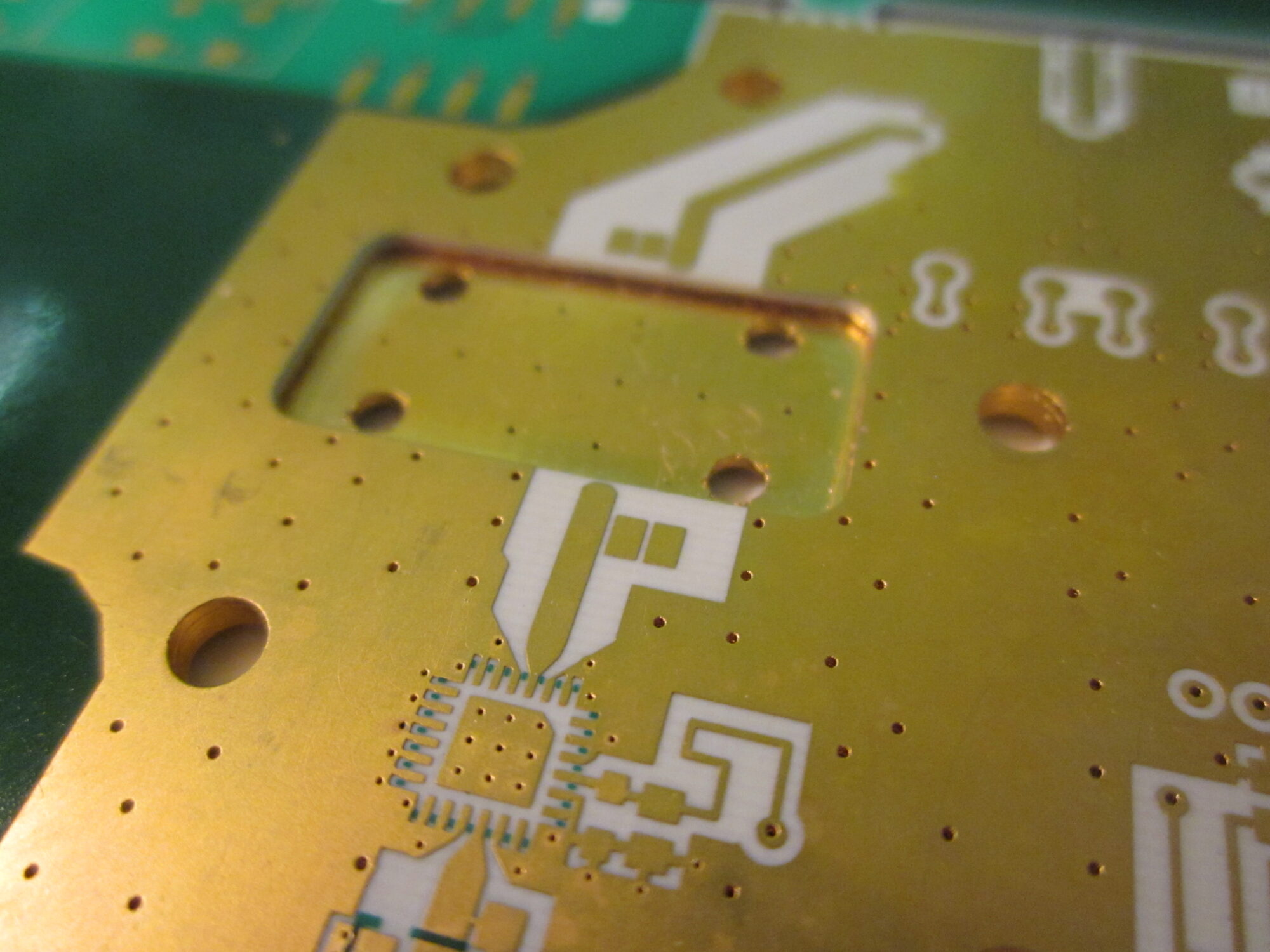
Example of a microwave implementation
- Drilling
- Microwave function
- SIW
- Patch antenna
- Microwave filter
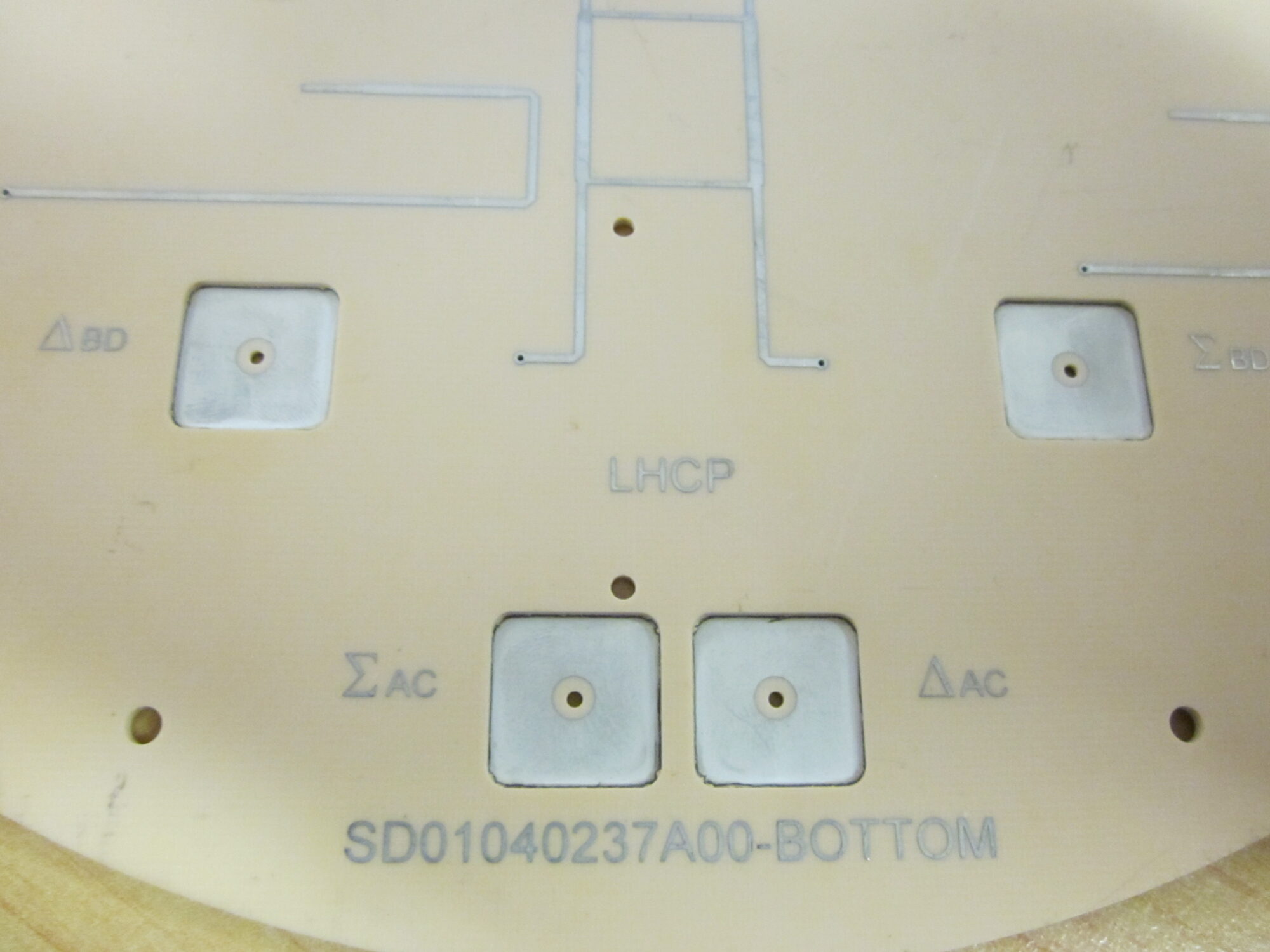
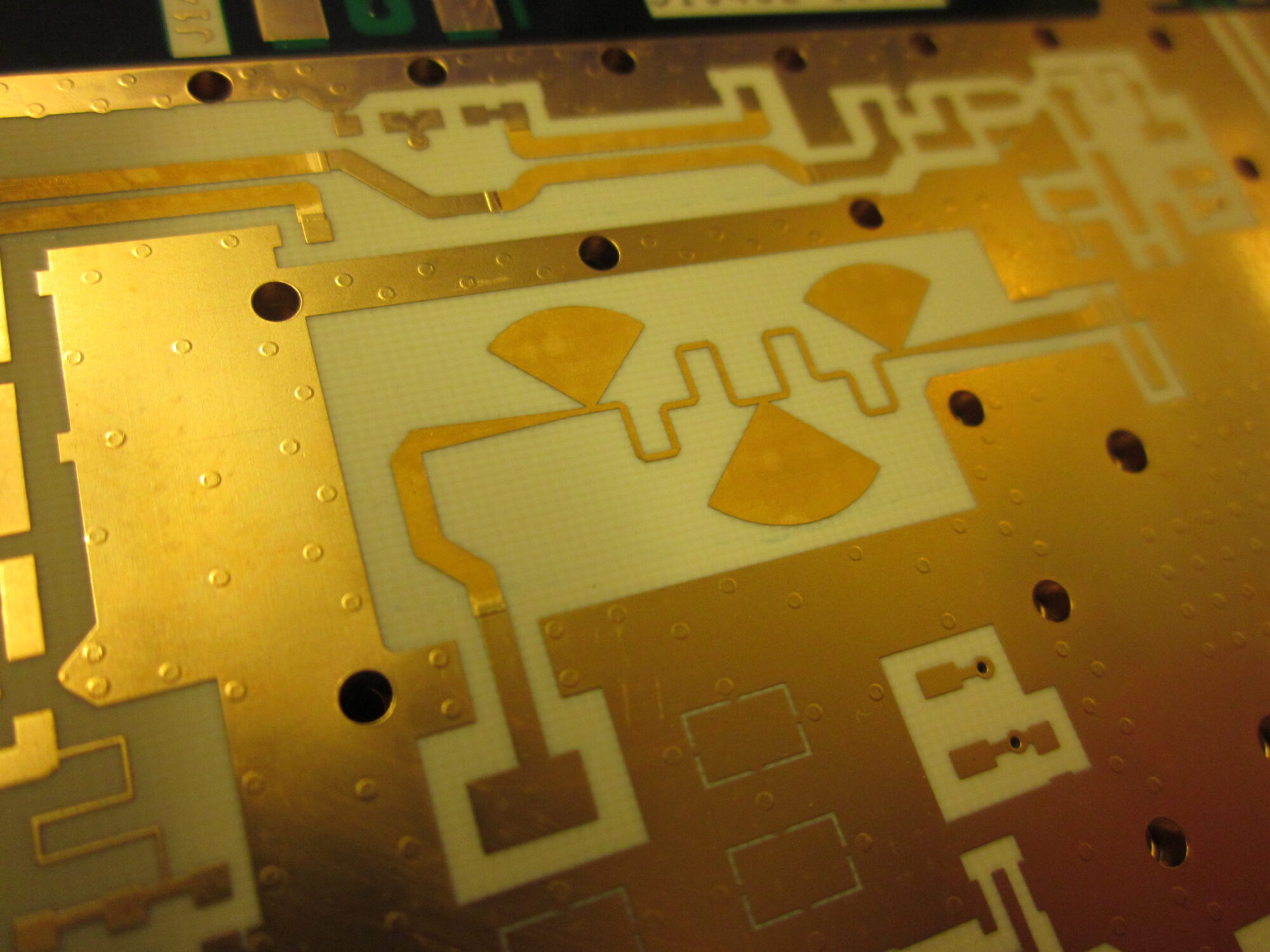
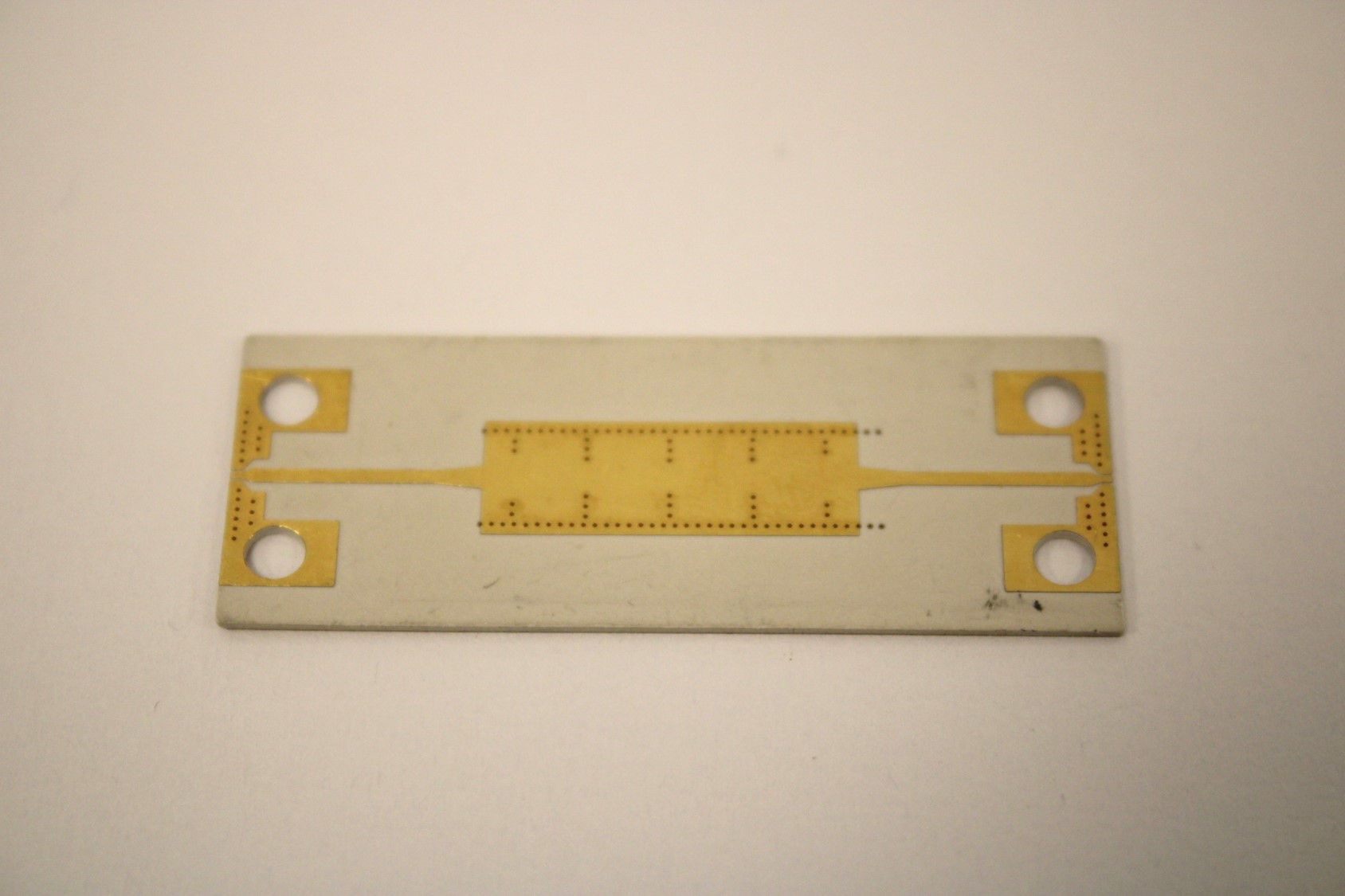

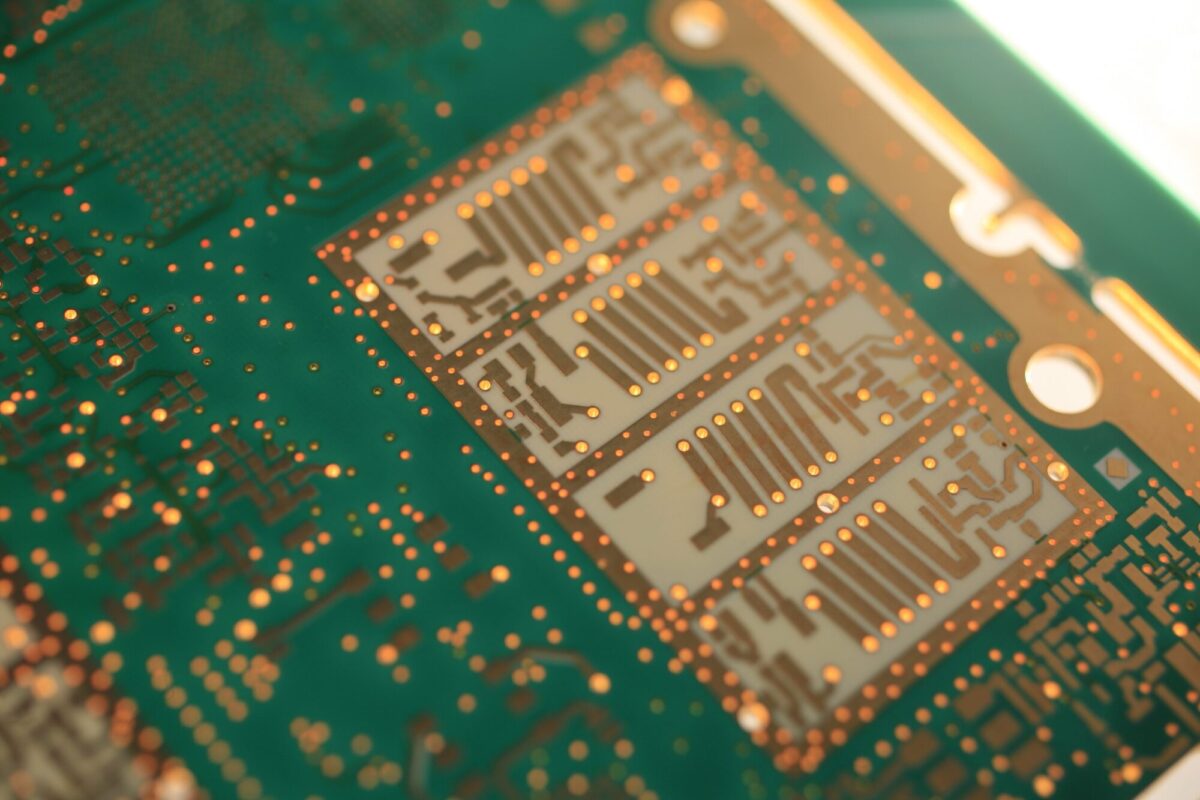
Examples of use:
- Defence
- Telecommunications (power amplifiers and antennas)
- RFID
- Medical
- Automotive (radar)
Foam materials
Microwave materials bonded to thick foam, selective etching on specific materials
Innovation R&D hybrid batch
Specific process adapted to microwave circuits
- Thermoset Prepreg
The standard bonding solution. With thermoset prepreg, the bonding, drilling and metal plating processes can be carried out as many times as required, unlike with thermoplastic film.
- Thermoplastic or Bondply film example: Arlon FV6700 or Dupont FEP
The choice of film to be used will depend on the melting point of the film and the temperatures to be applied to the circuit during the subsequent lamination. These films can be glued and unglued several times. Their main interest lies in their good dielectric performance (low losses) as well as their reduced thickness, which limits the RF impact of these bonding sheets.
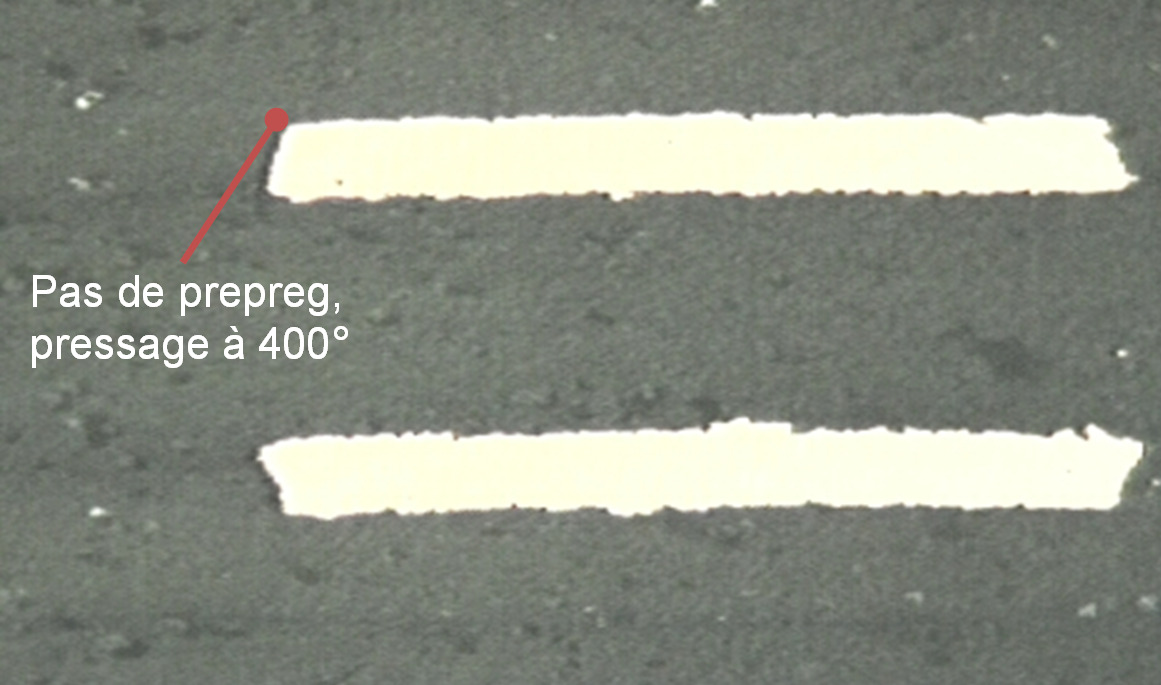
- Teflon fusion or direct bonding (PTFE lamination at 400°C) ensures dielectric homogeneity
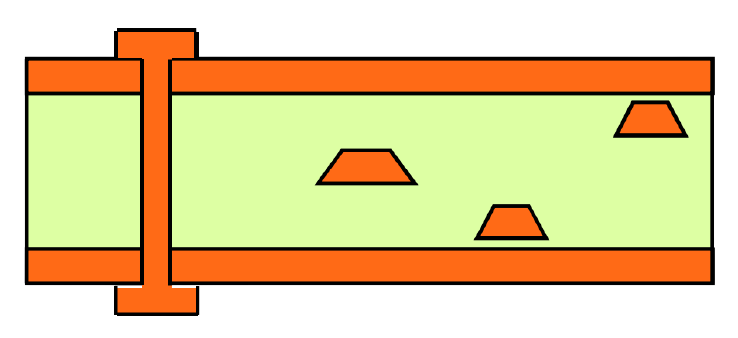

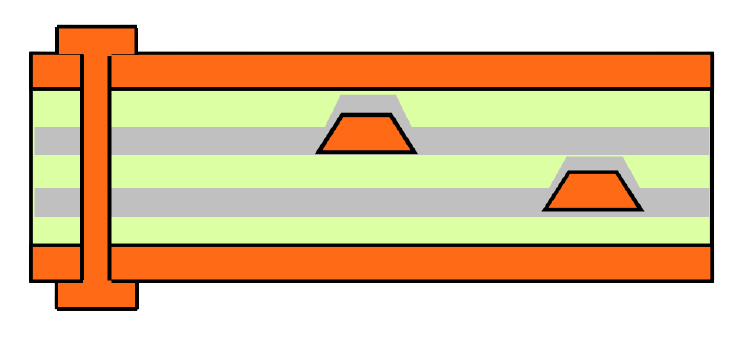
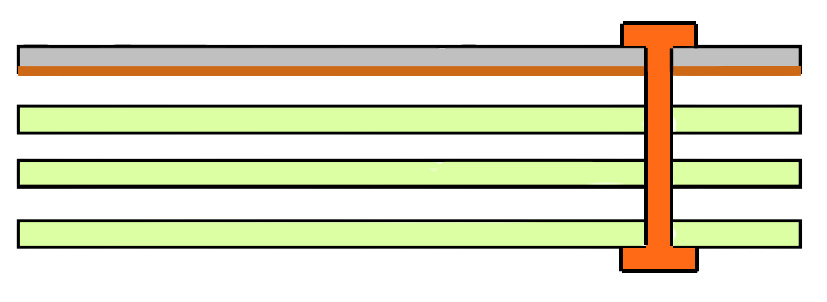
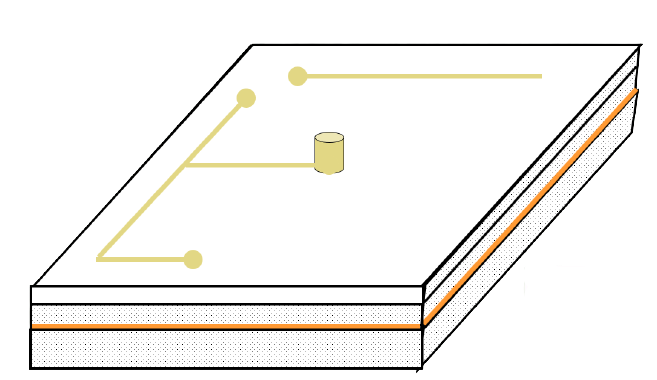
Stack example for microwave circuit
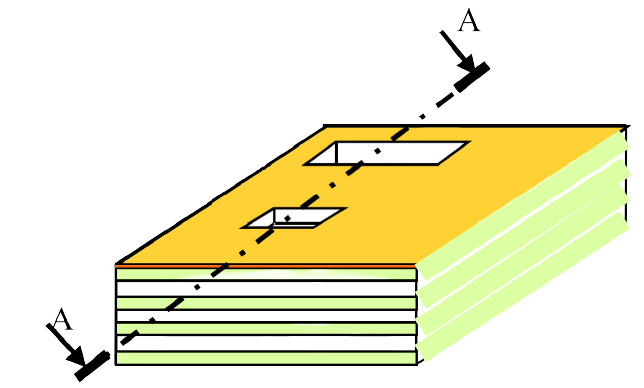
- Sequential PCB
- PCB mixed materials
- Triplate
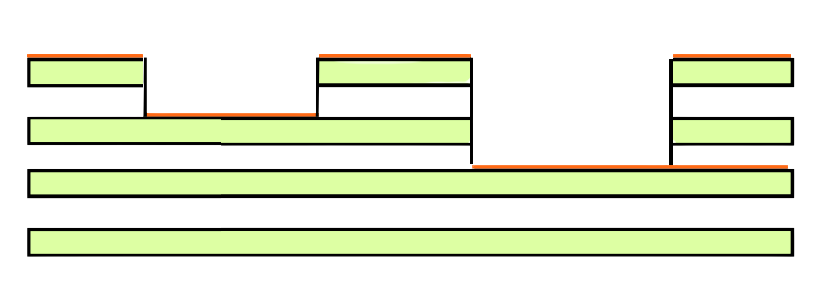
- Sequential well PCB
- Direct transfer to internal ground
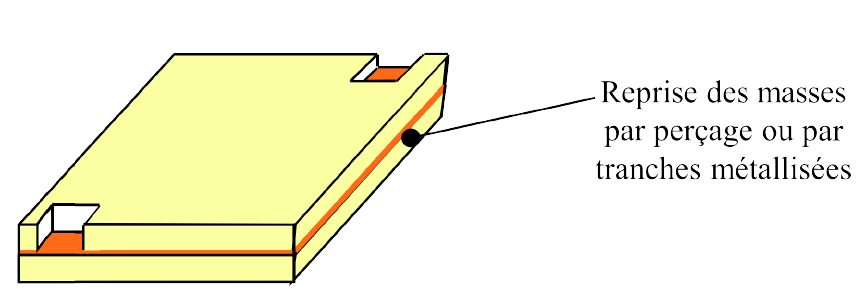
- Cavity with metal-plated walls
For further information, please contact us
 Attention, vous utilisez un navigateur peu sûr !
Attention, vous utilisez un navigateur peu sûr !